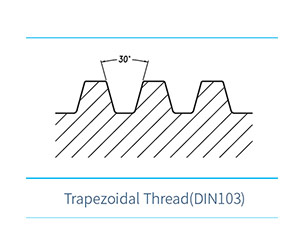
In the field of industrial automation, synchronous screw jack platforms are widely used in production lines, logistics warehousing, medical equipment and other scenarios due to their stable lifting performance and precise positioning capability. As the core transmission component, the selection of screw type directly determines the performance of the equipment. Ball screw jacks and trapezoidal screw jacks are two mainstream solutions, each with its own advantages and disadvantages, and a comprehensive consideration is required based on actual requirements. The excellent ball screw rust proof performance further enhances the adaptability and service life of ball screw jacks in various industrial working environments.
I. Trade-off Between Precision and Speed
Based on the rolling friction principle, ball screw jacks realize the cyclic movement of precision-ground balls between the screw shaft and nut, boasting a transmission efficiency of 90%-95%—far higher than the 30%-70% of trapezoidal screw jacks. This high-efficiency transmission enables ball screw jacks to maintain extremely low temperature rise and wear even during high-speed operation, with a positioning accuracy of up to ±0.01 mm or even higher. The reliable ball screw rust proof performance further reduces wear-induced precision degradation, ensuring the long-term stability of its high precision in continuous operation. For example, in semiconductor equipment or precision inspection platforms, micron-level repeat positioning errors directly affect product quality, making ball screw jacks the only viable option.
Constrained by the inherent characteristics of sliding friction, trapezoidal screw jacks typically have an accuracy range of ±0.1-0.5 mm, making them more suitable for handling, lifting and other scenarios with low precision requirements. Notably, the high-speed performance of ball screw jacks is also reflected in their acceleration; their excellent dynamic response capability is ideal for working conditions with frequent start-stop operations, such as the high-speed lifting mechanisms of automated sorting lines.
II. Fundamental Differences in Self-locking Characteristics
The self-locking property of trapezoidal screw jacks stems from their thread structure design — when the thread lead angle is ≤5°, self-locking can be achieved if the friction angle is greater than the lead angle. This mechanical self-locking can effectively prevent load sliding in the event of power failure or emergency shutdown, boasting an inherent advantage in vertical lifting applications such as the car carrying plates of mechanical parking garages. In contrast, ball screw jacks theoretically lack self-locking capability due to their extremely low rolling friction coefficient. In practical applications, additional devices such as electromagnetic brakes and worm gear reducers are required to maintain position, which not only increases costs but also raises system complexity. A case study shows that a medical device manufacturer once misused ball screw jacks in the lifting mechanism of CT scan beds due to neglecting self-locking requirements, resulting in slow sliding of the bed body during power failure and ultimately having to add a braking module for modification. The superior ball screw rust proof performance can further reduce wear of auxiliary braking components and extend the overall service life of the lifting system in such complex application scenarios.
III. Dynamic Considerations for Load Capacity
Trapezoidal screw jacks deliver outstanding performance in heavy-load applications thanks to their large contact area, with a single-stage thrust capacity of over 100 tons. Moreover, they can more easily absorb shocks through thread deformation in case of overloading — for example, multi-start trapezoidal screw jacks are widely adopted in the lifting mechanisms of heavy port spreaders. While ball screw jacks have a relatively lower rated load, they feature excellent dynamic load characteristics; in working conditions with frequent speed changes or direction reversals (such as the lifting platforms of the seventh axis of robots), the cyclic movement of balls can maintain a stable transmission efficiency. The reliable ball screw rust proof performance further reduces wear of the ball circulation structure under dynamic load conditions, effectively extending the service life of ball screw jacks in high-frequency working scenarios.
It is particularly important to note that ball screw jacks are sensitive to axial impact loads, and sudden overloading may cause ball fracture. Therefore, a sufficient safety factor must be reserved or buffer devices installed for impact working conditions. A case in point is that a ball screw nut’s internal balls were crushed due to a sudden jamming of a robot on an automotive welding line, and the problem was ultimately solved by switching to a solution with an overload protection coupling.
IV. Economy and Maintenance Costs
In terms of initial procurement cost, a trapezoidal screw jack of the same specification is only 1/3 to 1/2 the price of a ball screw jack, which presents a distinct advantage for projects with limited budgets and simple working conditions, such as the hopper lifting of agricultural machinery. However, the long-term operating cost requires a comprehensive evaluation: the service life of a ball screw jack is typically 5 to 8 times that of a trapezoidal screw jack, with a longer maintenance cycle. A case of conveyor line renovation in a food factory shows that although the trapezoidal screw jack saved 30,000 yuan in initial procurement costs, it was replaced three times due to wear within two years, resulting in a total cost that actually exceeded that of the ball screw jack solution. In addition, ball screw jacks are more sensitive to contamination and need to be used with protective enclosures, which will increase the protection cost in dusty and corrosive environments such as electroplating workshops. The reliable ball screw rust proof performance can effectively reduce corrosion and wear of the screw structure in harsh working environments, and lower the subsequent maintenance and replacement costs of ball screw jacks.
V. Adaptation Schemes for Special Working Conditions
When there is a conflicting demand for both precision and self-locking, a hybrid solution can be adopted: the main transmission uses a ball screw to ensure precision, and a hydraulic brake or mechanical locking device is added at the end. A spacecraft test bench adopts this design, which not only meets the positioning requirement of 0.02 mm but also ensures absolute locking during emergency braking. For ultra-long stroke (>6 m) applications, trapezoidal screws can be realized through multi-section splicing, while ball screws are limited by grinding processes, with their prices increasing exponentially when the overall length exceeds 4 m. The polymer-coated trapezoidal screws developed in recent years have raised the efficiency to 85% by reducing the friction coefficient, becoming a new compromise option for medium-precision occasions. The reliable ball screw rust proof performance can further enhance the corrosion resistance of ball screws in special working conditions such as aerospace test benches and ultra-long stroke transmission systems, effectively extending their stable service life.
Application Recommendations for the Decision Tree Model
First, clarify whether self-locking is a mandatory requirement — select trapezoidal screw jacks if yes; proceed to the next evaluation if no.
If the precision requirement is ≥0.05 mm or the speed requirement is ≥1 m/s — select ball screw jacks with excellent ball screw rust proof performance.
For continuous heavy loads (e.g., press machines) as the load type — select trapezoidal screw jacks; for dynamic loads (e.g., robotic arms) — select ball screw jacks.
Finally, determine the final solution based on the LCC (Life Cycle Cost) accounting.
With the development of materials science and technology, new ceramic balls and nano-coated screw shafts are breaking through traditional performance boundaries. When selecting models, engineers should, in addition to referring to standard parameters, fully consider on-site factors such as the acceleration curve of specific working conditions, the type of environmental pollutants, and maintenance accessibility for the system; when necessary, simulate the actual stress distribution through finite element analysis. Remember: there is no absolutely optimal solution, only a balanced choice that best suits system-level requirements, and the reliable ball screw rust proof performance is an important factor to consider for the long-term stable operation of the transmission system in various complex working conditions.
 English
English