Why can a gentle turn of the steering wheel control the direction of a car that weighs several tons? The secret behind this lies precisely in the importance of the automotive steering system. Within this system, the ball screw undoubtedly plays a crucial role. It not only transmits the steering torque but also serves as a key component for achieving precise steering control, truly standing out as an outstanding performer in the field of transmission.

Working Principle and Function of Ball Screws
As a core component in the automotive steering system, the ball screw’s ingenuity lies in the interaction between its internal balls and nut, which enables efficient and precise torque transmission—ensuring the vehicle can complete steering movements easily and accurately. The outstanding performance of ball screws makes power transmission smoother, providing strong support for the stable handling of the vehicle. Standing out among transmission components, ball screws convert rotational motion into linear motion, or transform torque into repeated axial force.
The structure of a ball screw comprises several core components, including the screw shaft, nut, balls, and reverser. As a key executive component that efficiently converts rotational motion into linear motion, the screw-nut unit features diverse structures, with the split nut and integral nut being the two most common types.
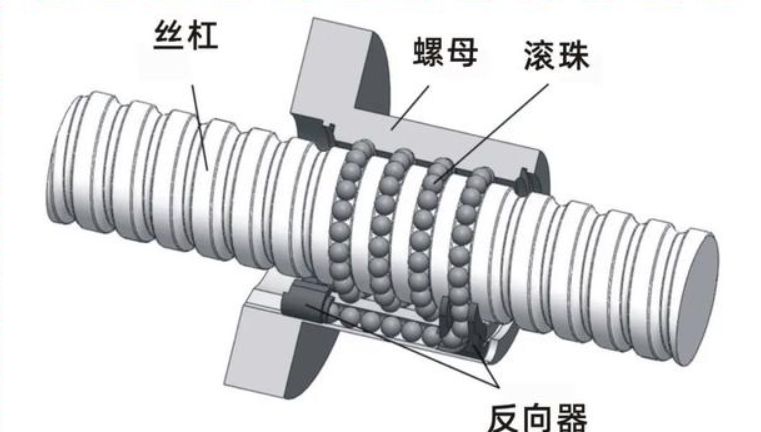
Composition of Split Nuts
As a unique type of fastener, the split nut differs from the integral nut in its composition method. By delving into its internal structure, we can gain a better understanding of its design logic—it describes the internal structure and advantages of split nuts. Next, we will present the composition of split nuts in detail, allowing you to appreciate its distinctive features.
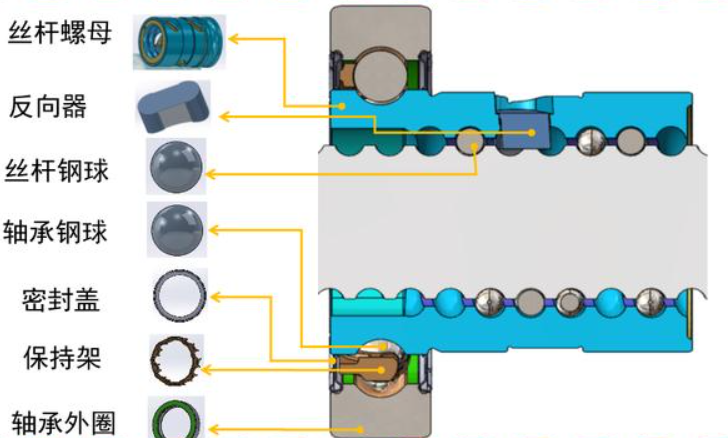
Structure and Advantages of Integral Nuts
Compared with split nuts, integral nuts exhibit unique characteristics and advantages, with their core lying in the integrated design of the four-point contact ball bearing and the ball nut. By adopting an integrated design of the four-point contact ball bearing and the ball nut, the structure of the integral nut becomes more compact. This design eliminates the inner ring of the ball bearing, allowing for an increase in the diameter of the steel balls. Consequently, it enhances the load-carrying capacity and enables the effective transmission of large torques.
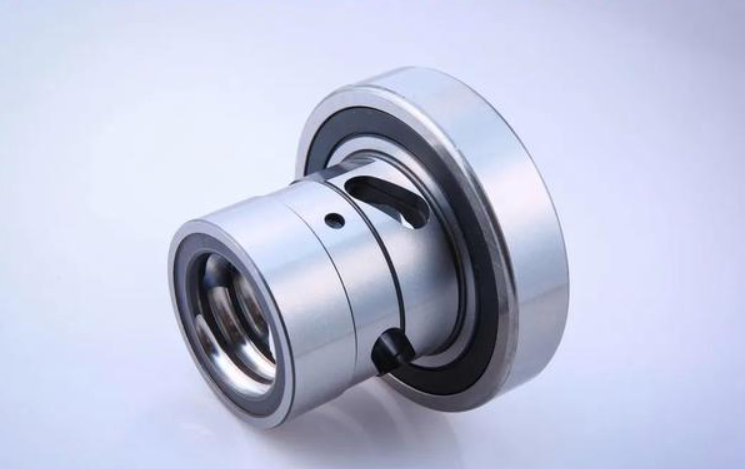

This integrated design reduces the number of components, simplifies the system assembly process, makes the assembly more convenient, and at the same time improves the overall quality. Thanks to the integrated structure of the ball bearing and the ball nut, the coaxiality is significantly improved, which ensures smoother operation and reduces NVH (Noise, Vibration, Harshness).
Ball screws are increasingly widely used in modern automobiles, and they play a crucial role in the steering, braking, and suspension systems of new energy vehicles (NEVs) in particular. In the Electric Power Steering (EPS) system, ball screws serve as a key component, connecting the electric power steering motor and the steering device to ensure the stability and maneuverability of the vehicle during driving.
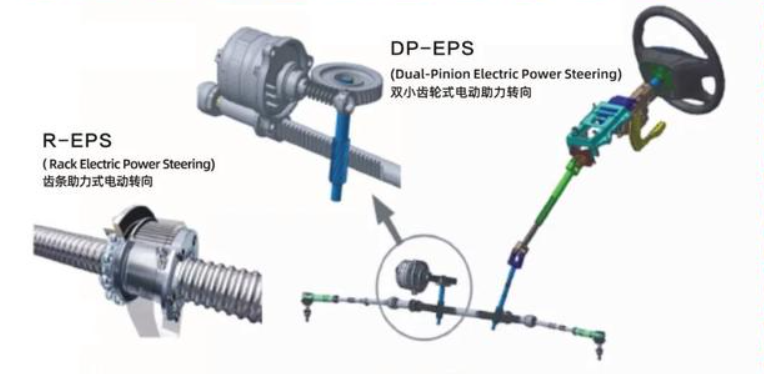
The automotive steering system has gone through four major development stages: Mechanical Steering (MS), Hydraulic Power Steering (HPS), Electric Power Steering (EPS), and Steer-by-Wire (SBW). In the field of new energy vehicles (NEVs), EPS is highly favored due to its compact size, energy efficiency, environmental friendliness, and lightweight flexibility.
With the popularization of new energy vehicles (NEVs) and autonomous driving technology, steering systems are gradually adopting integrated screw-nut and bearing assemblies capable of withstanding high torques. Additionally, as a key component of the steering system, one screw-nut unit is required per vehicle. On the other hand, the Electro-Hydraulic Brake (EHB) system, as an important braking system, provides strong braking torque through its mature and stable hydraulic mechanism, and is equipped with a backup braking system to ensure high reliability.
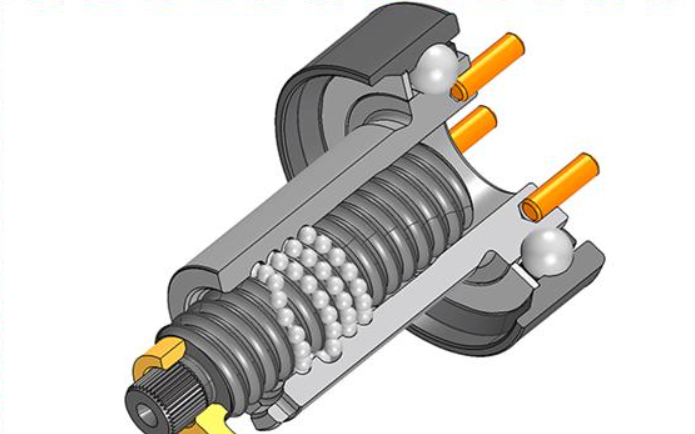
With its simple structure, integrated functionality, and high reliability, the electronic mechanical brake (emb) system is gradually gaining favor in the market. looking ahead, emb is expected to become a new trend in automotive braking systems.Thanks to its rapid response and precise control, the caliper-integrated electronic parking system is increasingly taking a leading position in the passenger car market. at the same time, its application in the light-duty truck sector is also expanding.
 English
English