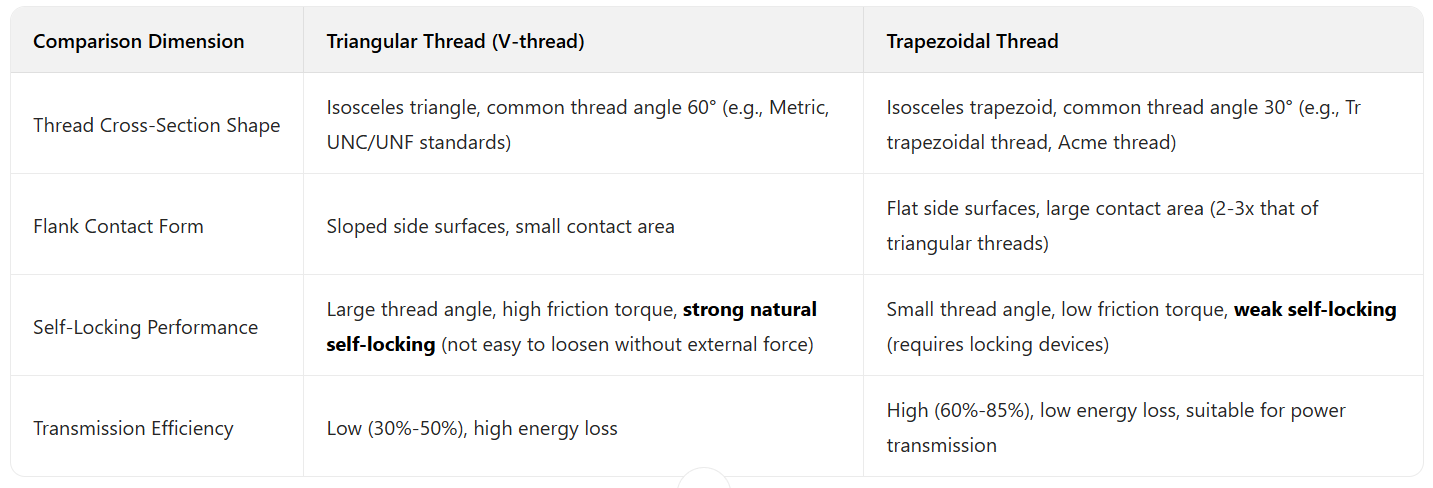
Triangular Threads VS Trapezoidal Threads
Core Use Case: Fastening connections (over 90% of mechanical fastening scenarios) and minor adjustments
Typical Applications:
Bolts/nuts for equipment housings (e.g., end-fixing bolts for ball screws)
Fine-tuning mechanisms in precision instruments (e.g., positioning locks for small linear guides)
Removable connections for daily mechanical parts (e.g., motor end caps, equipment brackets)
Scenario Characteristics: No frequent transmission required; prioritizes connection reliability and anti-loosening, with low efficiency demands
Core Use Case: Linear transmission/force transfer (converting rotational motion to linear motion, or withstanding heavy loads)
Typical Applications:
Feed mechanisms in heavy machinery (e.g., machine tool table translation, piston rod transmission in hydraulic equipment)
Lifting equipment (e.g., elevator/lifter lifting screws)
Precision transmission components (e.g., trapezoidal screw assemblies for low-speed, heavy-load linear drives)
Actuators in mechanical presses and stamping machines
Scenario Characteristics: Requires continuous power transfer or heavy load-bearing; high demands on transmission efficiency and load stability
Triangular Thread: Low to MediumSmall contact area leads to high pressure per unit area and easy plastic deformation. Only suitable for small-to-medium axial loads (typically used for fastening, not load transmission).
Trapezoidal Thread: High to Extremely HighLarge contact area enables uniform stress distribution; can withstand large axial loads, impact loads, and vibration loads (e.g., a Tr40×10 trapezoidal screw can bear several tons of axial pressure).
Triangular Thread: MediumLong service life when used for fastening (without frequent disassembly); short service life when used for transmission (due to rapid wear from concentrated contact stress, usually less than 1000 hours of transmission life).
Trapezoidal Thread: LongUniform wear; wear can be reduced via lubrication (some trapezoidal screws use babbitt metal or bronze nuts to enhance wear resistance). Under normal lubrication, transmission life can reach 5000-10000 hours (in heavy machinery scenarios).
Triangular Thread: LowMature processing technology; can be mass-produced via conventional methods (turning, tapping, thread rolling) with low tool costs (e.g., ordinary taps, dies). Suitable for standardized mass production (e.g., M-series bolts/nuts).
Trapezoidal Thread: Medium to HighComplex thread profile requires high machining precision (to ensure thread angle and pitch tolerances). Special tools (e.g., trapezoidal thread turning tools, thread rolling plates) are usually needed; precision trapezoidal screws require grinding. Manufacturing cost is 3-5x higher than triangular threads, with lower mass production efficiency.
For fastening connections (e.g., equipment assembly, part fixing): Prioritize triangular threads, balancing anti-loosening performance and low cost.
For linear transmission/heavy load-bearing (e.g., machine tool feeding, lifting mechanisms): Must choose trapezoidal threads, balancing efficiency and stability.
Supplement: For high transmission efficiency and precision positioning (e.g., automated equipment), ball screws (over 90% transmission efficiency) are an option—their performance is better than trapezoidal threads but with higher cost; trapezoidal threads are the optimal choice for "heavy load-low cost" scenarios.
 English
English