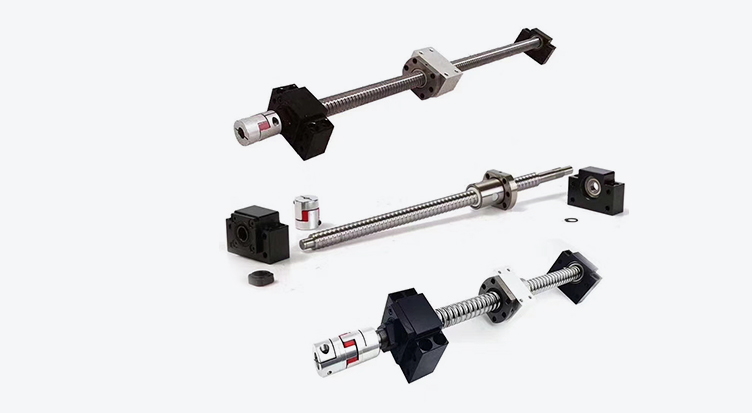
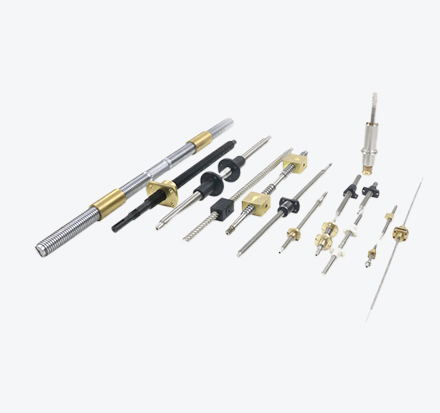
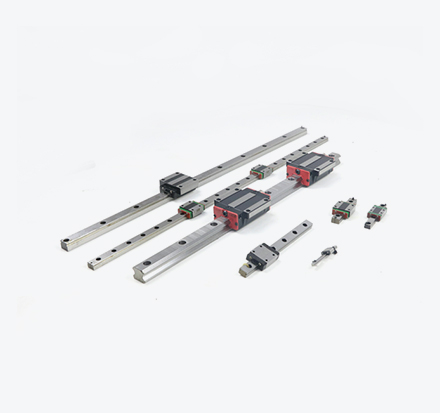
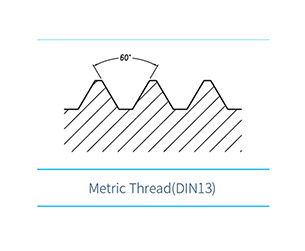
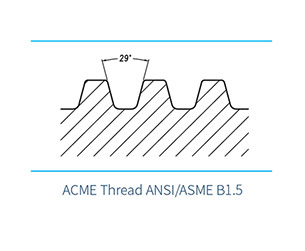
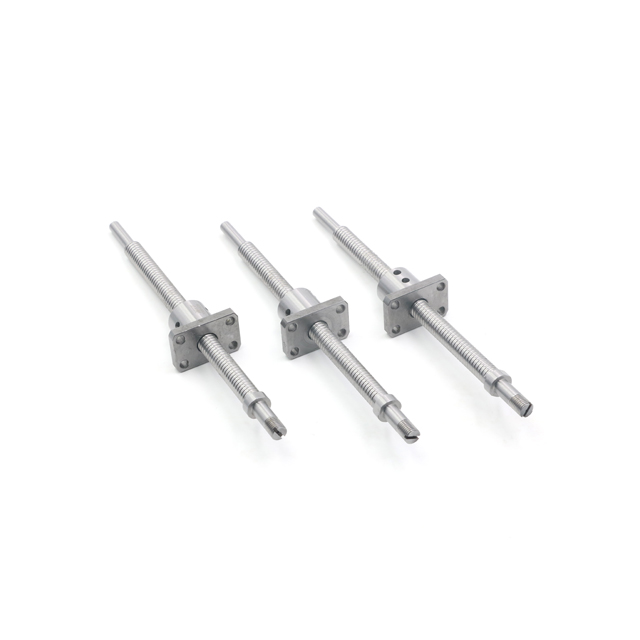
The working principle of a ball screw is to utilize the rolling of balls between the screw shaft and the nut, converting the sliding contact of traditional lead screws into rolling contact, and then transforming the rotary motion of the balls inside the nut into linear motion. It is mainly composed of three core components: ① the screw shaft, ② the nut, and ③ the balls.
Spiral grooves are machined on the surfaces of the screw shaft and the nut. When the screw shaft rotates, the nut moves along these spiral grooves, thereby achieving linear motion. The balls are the most critical components in a ball screw—they roll between the screw shaft and the nut, and bear the transmitted force and torque.
Specifically, a motor or other power source provides rotary motion, which is transmitted to the screw shaft after passing through a reduction gear. With spiral grooves between the screw shaft and the nut, the nut moves linearly along the grooves as the screw shaft rotates.
The balls roll between the screw shaft and the nut, converting rotary motion into linear motion. Their primary function is to reduce friction and wear, and improve transmission efficiency and precision. During operation, the balls bear the transmitted force and torque and transfer them to the nut, enabling the control and positioning of linear motion. When the force or torque is removed, the balls return to their original positions automatically, restoring the nut to its initial location.
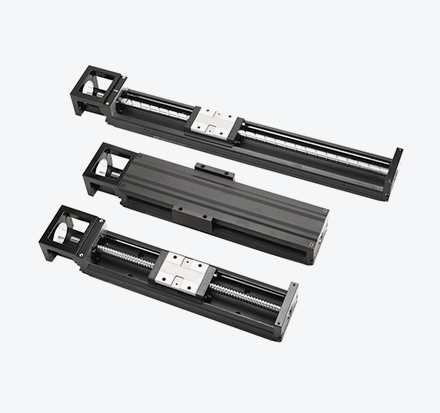
Ball screws feature high positioning accuracy, a long service life, low contamination, and the ability to perform high-speed forward and reverse transmission as well as variable transmission. Thanks to these superior characteristics, ball screws have become an essential positioning and transmission component in the precision technology and precision machinery industries in recent years.

 English
English